Cyber threats have evolved beyond traditional hacking techniques. Today, one of the most dangerous forms of cybercrime is social engineering, a psychological manipulation tactic used to trick employees into divulging confidential information, transferring funds, or granting access to critical systems.
According to the Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, 74% of cybersecurity breaches involve human elements, including social engineering attacks. As businesses increasingly rely on digital communication, cybercriminals are exploiting human trust and behavior to bypass security defenses.
Understanding social engineering: how cybercriminals exploit human nature
Unlike traditional cyberattacks that rely on technical vulnerabilities, social engineering attacks exploit human psychology. Instead of hacking into a system, attackers manipulate employees into unknowingly providing access.
Common tactics include:
- Impersonation: Attackers pose as executives, IT staff, or suppliers to request sensitive data or financial transactions.
- Urgency & Fear Tactics: Hackers create a sense of emergency, pressuring employees into acting quickly without verification.
- Pretexting: Cybercriminals fabricate scenarios, such as fake audits or compliance checks, to extract confidential information.
These methods are increasingly sophisticated, making them harder to detect than traditional cyber threats.
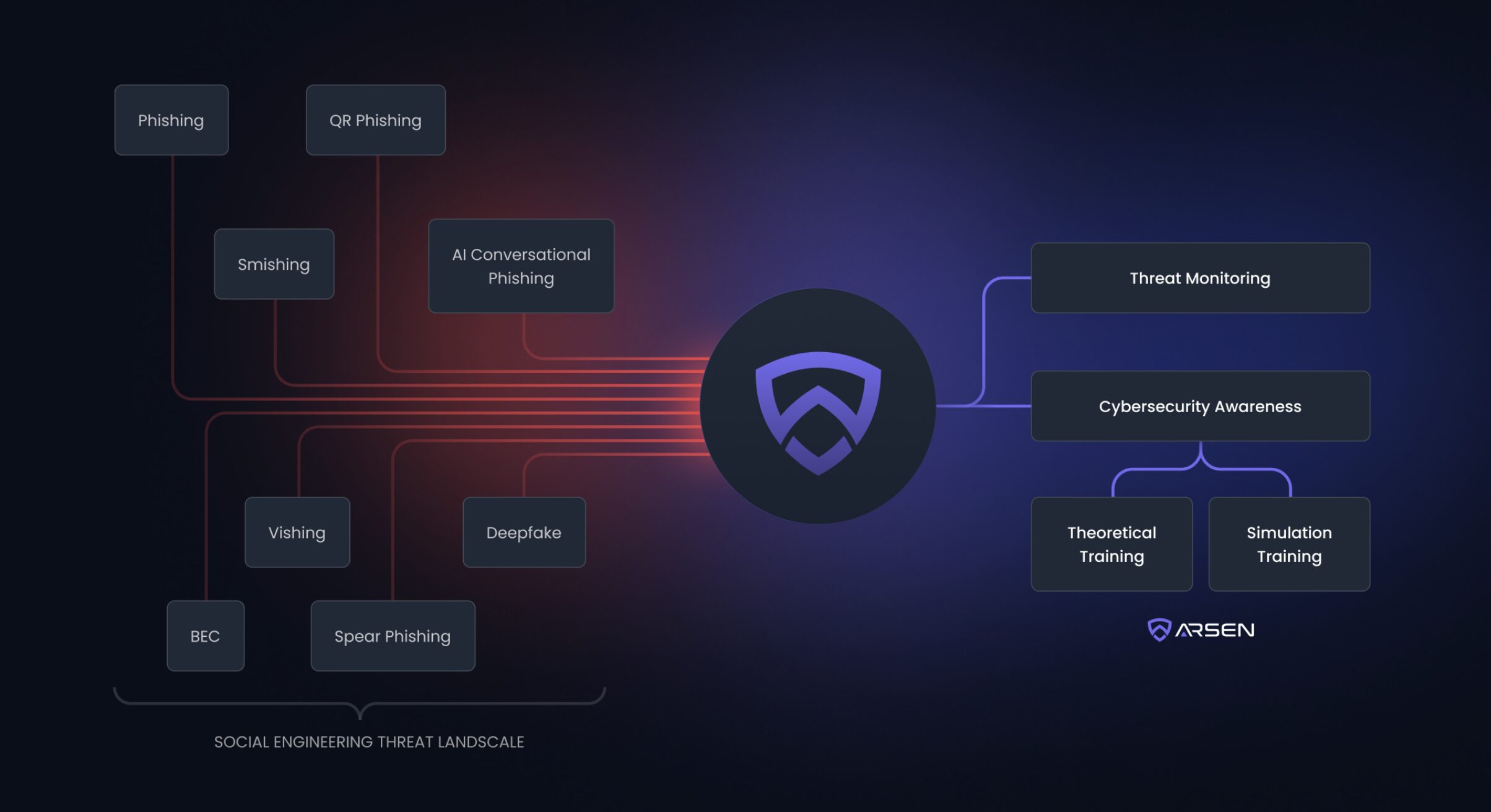
Top 10 most common social engineering attacks
- Phishing Emails: Fraudulent emails that impersonate trusted sources to steal credentials.
- Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks against specific employees using personal details to increase credibility.
- CEO Fraud (Whaling): Attackers impersonate executives to request urgent wire transfers.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Fraudulent calls from attackers pretending to be IT support or bank representatives.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Text messages containing malicious links or fake security alerts.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Cybercriminals hijack business email accounts to send fraudulent requests.
- Baiting: Attackers leave infected USB drives or malicious links disguised as free downloads.
- Quid Pro Quo Attacks: Fraudsters offer fake technical support to trick employees into revealing credentials.
- Tailgating (Physical Social Engineering): Attackers gain unauthorized access to offices by following employees through security checkpoints.
- Deepfake Scams: AI-generated voice and video impersonations used to manipulate employees into taking action.
How to protect your business against social engineering attacks
Since social engineering attacks exploit human behavior rather than software vulnerabilities, education and awareness are key to prevention. Here are the most effective strategies:
- Cybersecurity awareness training: Employees should be trained to recognize social engineering tactics and follow best practices for verifying requests.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Reducing reliance on passwords alone makes it harder for attackers to access sensitive systems.
- Zero-trust security model: Organizations should limit access to critical data, ensuring employees only have permissions necessary for their roles.
- Strict verification protocols: Any sensitive request (e.g., wire transfers, credential changes) should require multi-step verification through independent channels.
- Simulated social engineering attacks: Businesses can proactively test their employees’ awareness with social engineering attack simulations to reinforce security measures.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, up from $3 trillion in 2015. This estimate includes various cyber threats, such as ransomware, data breaches, and social engineering attacks, highlighting the urgent need for proactive cybersecurity measures.
Final thoughts
Social engineering is one of the most dangerous and evolving cybersecurity threats, preying on human psychology rather than system vulnerabilities. Businesses that fail to educate their employees or implement strict security measures risk financial losses, data breaches, and reputational damage.
By prioritizing cybersecurity awareness training and simulated attack scenarios, organizations can strengthen their defenses and significantly reduce their risk exposure.