Today, credit cards have become a go-to payment method for millions of people worldwide. Whether you’re shopping online, paying at a restaurant, or buying groceries, credit cards offer a fast and convenient way to pay. But have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you swipe, tap, or insert your card? Let’s break down the process in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Step 1: The Customer Makes a Purchase
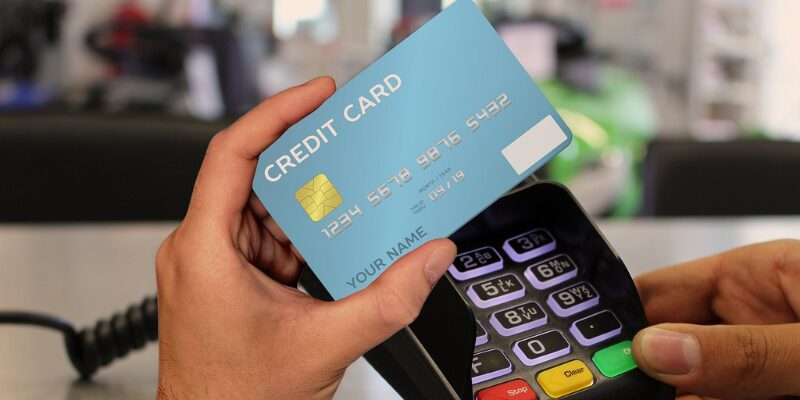
The credit card payment process starts when a customer decides to buy something using their card. This could happen in a physical store using a card reader or online through a website or mobile app.
When the card is swiped, tapped, or entered online, the payment details (card number, expiration date, CVV code) are sent securely to begin the transaction.
Step 2: The Payment Gateway Transmits the Information
Once the customer initiates the payment, the payment gateway comes into play. Think of the payment gateway as a digital middleman that securely transfers transaction details from the merchant’s system to the payment processor.
For online transactions, the payment gateway ensures that sensitive data is encrypted and transmitted safely to prevent fraud or data theft.
Step 3: The Payment Processor Works Behind the Scenes
After the payment gateway sends the transaction details, the payment processor steps in. The processor is responsible for forwarding the request to the customer’s bank (also known as the issuing bank) to check if there are enough funds or available credit for the transaction.
At this point, the processor is working in real time, communicating with different financial institutions to determine whether the transaction can be approved.
Step 4: The Card Network Approves or Declines the Payment
Credit card transactions involve major card networks such as Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover. These networks act as traffic controllers, making sure the payment request is routed properly between the merchant, the customer’s bank, and the business’s bank.
The card network also ensures that all necessary security checks are completed to prevent fraudulent transactions.
Step 5: The Issuing Bank Reviews the Transaction
The customer’s bank (issuing bank) then takes over. It checks several factors, including:
- Whether the customer has enough funds or available credit.
- Whether the card is valid and not blocked.
- If the transaction seems suspicious or unusual.
If everything looks good, the bank approves the transaction. If there are issues like insufficient funds, incorrect details, or suspected fraud—the transaction is declined.
Step 6: The Merchant Receives the Payment Approval
If the issuing bank approves the transaction, the approval message is sent back through the same path from the bank, through the card network, payment processor, and finally, back to the merchant’s payment system.
At this point, the merchant’s system processes the payment, and the customer is notified that the transaction was successful.
Step 7: Settlement and Funds Transfer
Approving the transaction is only half of the process. The actual transfer of money from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s bank (acquiring bank) happens during a process called settlement.
Settlement usually occurs at the end of the business day when the merchant batches all approved transactions and submits them for processing. The acquiring bank then deposits the funds into the merchant’s account, typically within 1-3 business days.
Fees Involved in Credit Card Processing
Credit card transactions aren’t free merchants have to pay a small percentage of each transaction as processing fees. These fees are usually divided among the payment processor, the card network, and the issuing bank.
Common fees include:
- Interchange Fees – Paid to the customer’s bank for processing the payment.
- Assessment Fees – Paid to the card network (Visa, Mastercard, etc.).
- Payment Processor Fees– Paid to the processor for handling the transaction.
Why Understanding Credit Card Processing Matters
Knowing how credit card processing works is important, especially if you’re planning to start a business or work in e-commerce. Here’s why:
- Security– Understanding the process helps you recognize fraud risks and how to protect against them.
- Costs– Merchants can make informed decisions about processing fees and choose cost-effective solutions.
- Customer Experience– A smooth payment process leads to a better shopping experience for customers.
Conclusion
Credit card processing may seem complex, but at its core, it’s a fast and secure way to transfer money between customers and businesses. With multiple steps happening in just a few seconds, modern technology ensures that transactions are completed safely and efficiently.
Whether you’re a shopper or a business owner, understanding this process can help you make better financial decisions and improve your digital payment experience.