In the fast-paced world of healthcare, the integration of diverse information systems has emerged as a pivotal challenge. Researcher Subrahmanyasarma Chitta has been a proponent of The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) as a comprehensive approach designed to streamline the integration of healthcare systems. By offering a structured methodology for enterprise architecture, TOGAF is set to revolutionize how healthcare organizations manage their IT infrastructures and align them with complex regulatory landscapes.
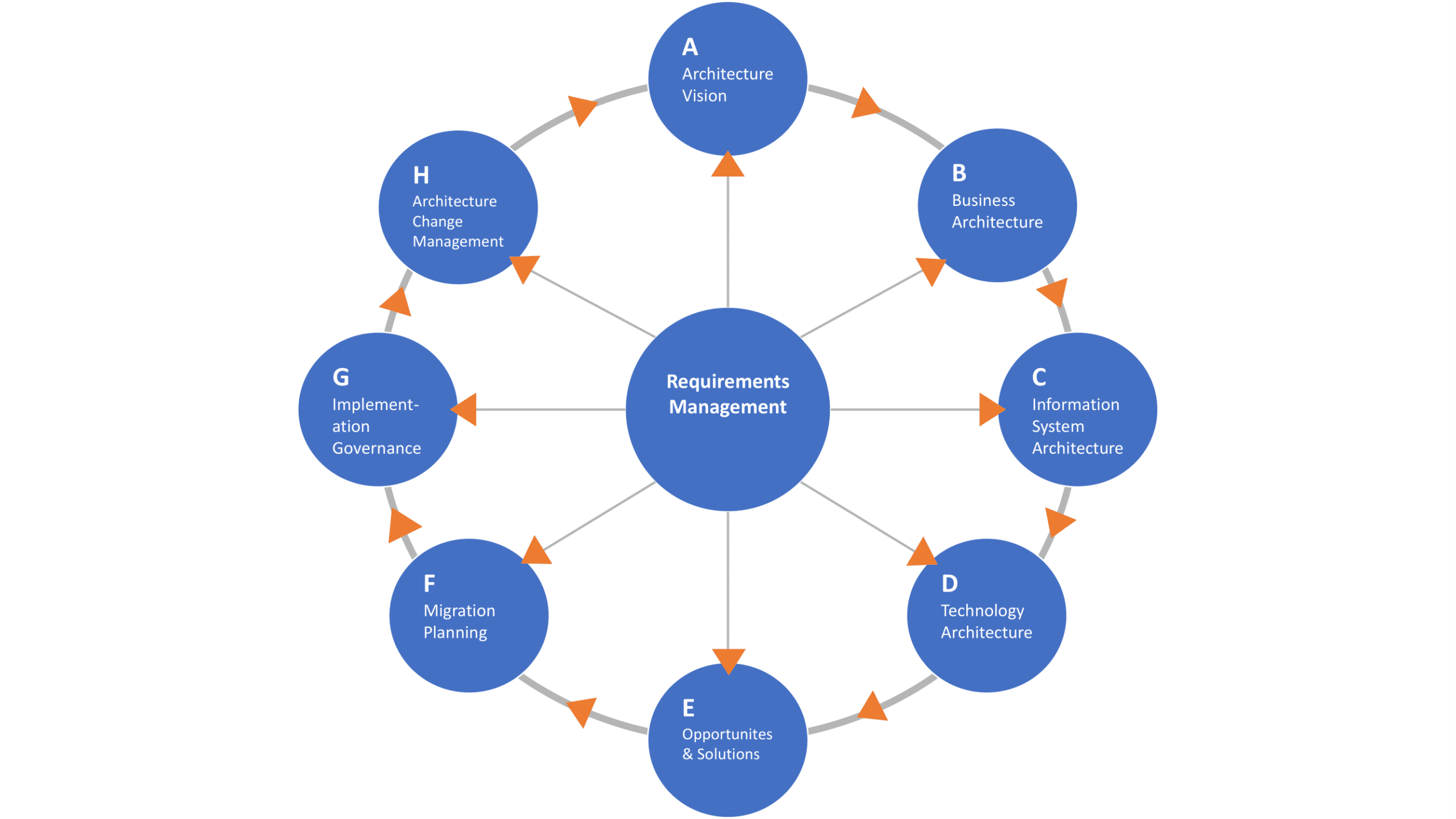
TOGAF’s methodology, known as the Architecture Development Method (ADM), is at the heart of its effectiveness. This robust framework comprises several key phases, including architecture vision, business architecture, information systems architecture, technology architecture, opportunities and solutions, migration planning, implementation governance, and architecture change management. Each phase plays a critical role in ensuring that healthcare systems can communicate seamlessly, share vital patient information, and meet the rigorous demands of regulatory compliance.
What distinguishes TOGAF is its emphasis on modularity and adaptability. Healthcare organizations often struggle with fragmented systems that hinder effective data sharing and operational efficiency. TOGAF promotes interoperability, enabling disparate systems to work together cohesively—a necessity in a field where timely access to patient data can significantly impact care outcomes.
The benefits of implementing TOGAF extend beyond mere efficiency; they encompass improved governance and compliance. For organizations operating under stringent regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, having a structured framework like TOGAF is essential for ensuring ongoing compliance. Its governance structures guide organizations in developing compliant architectures, thus alleviating the risks associated with data privacy breaches and regulatory violations.
An important aspect of TOGAF is its adaptability to emerging technologies. As the healthcare landscape evolves to embrace advancements such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), TOGAF remains relevant. Its modular approach allows healthcare organizations to integrate new technologies without overhauling existing infrastructures, promoting an agile response to industry shifts.
The incorporation of TOGAF into health IT frameworks is demonstrated through various real-world applications. Organizations that have adopted TOGAF have successfully aligned their IT systems with clinical workflows, resulting in unified electronic health record (EHR) systems that streamline data sharing across departments. These case studies emphasize the importance of robust stakeholder engagement in ensuring that implemented solutions meet the operational needs of healthcare providers while enhancing patient care.
Despite its advantages, the journey toward implementing TOGAF in healthcare is not without challenges. The complexity of integrating legacy systems, resistance from stakeholders, and the intricacy of aligning existing infrastructures with new technological opportunities can present significant barriers. Addressing these challenges requires strategic change management, continuous stakeholder engagement, and comprehensive training programs that highlight the benefits of adopting a structured architectural approach.
The potential for TOGAF to transform healthcare systems is vast. It provides a foundation for organizations to streamline operations and design future-proof architectures that can evolve alongside technological advancements. As healthcare increasingly leverages digital technologies, adopting frameworks like TOGAF will be crucial for maintaining high-quality patient care and operational efficiency.
Additionally, TOGAF’s support for collaborative efforts among various stakeholders is instrumental. Involving clinicians, administrators, IT professionals, and even patients in the architecture design process ensures that resulting systems align with real-world needs and expectations. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership among stakeholders, ultimately enhancing the adoption of new systems and technologies.
Looking ahead, the integration of TOGAF into healthcare systems underscores a new era of possibility. As organizations increasingly rely on advanced technologies, the demand for streamlined, interoperable systems will continue to grow. The principles established by TOGAF can serve as a blueprint for developing innovative healthcare solutions that prioritize patient data security, operational efficiency, and compliance.
In conclusion, the work of Subrahmanyasarma Chitta in promoting The Open Group Architecture Framework signifies a transformative approach to modernizing healthcare systems integration. His emphasis on TOGAF’s structured yet flexible methodology empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of the healthcare landscape effectively. By enhancing interoperability, ensuring compliance, and fostering stakeholder engagement, TOGAF is poised to redefine how healthcare organizations approach their IT frameworks. Innovations like these remind us of the power of technology to make a real difference in healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.