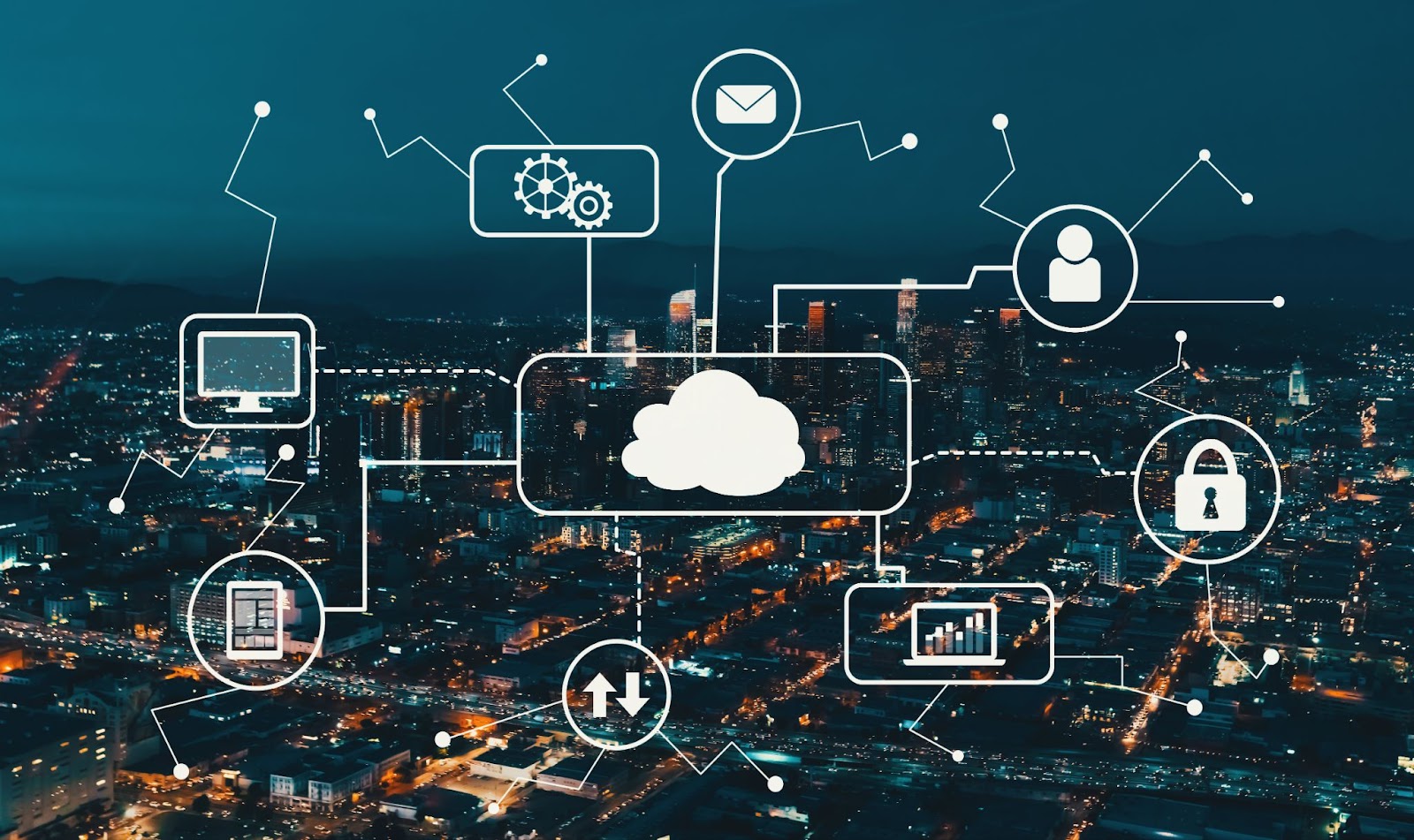
Cloud computing, the evolutionary technology that takes the concept of distributed systems to a different level, has become a driving force in the modern internet space, impacting how computer systems interact with one another and end users. In simple terms, cloud computing allows users to perform computing actions and access a wide range of services through computer resources, networks, data storage systems, servers, apps, and other tools stored on the cloud (the internet).
Cloud technology provides dynamically scalable virtual resources via the internet, allowing users to access computer hardware, software, and infrastructure instead of relying on local resources.
The history of cloud computing dates back to the 1950s when scientists conceptualized distributed systems, but its modern history began in the late 1990s and became mainstream in 2006. The evolution moved from mainframe computing to cluster and grid computing and virtualization. The jump to Web 2.0, utility computing, and virtualization greatly shaped the evolution of cloud computing from the days of distributed systems limited by physical proximity.
Core Concepts of Cloud Computing
At the core of cloud computing are concepts like service models and deployment models. There are three popular service models: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (Paas), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Service models describe the way that cloud providers deploy the technology for end users: Public, Private, Hybrid, and Multi-cloud. Scalability, elasticity, virtualization, cost management, fault tolerance, data security and compliance, APIs and integration, and high availability are also important concepts in cloud computing.
All cloud services offer on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, measured service, and scalability, allowing organizations the flexibility they need to build, deploy, and maintain solutions over the cloud.
Cloud Optimization and Management
Cost Optimization Techniques. Identifying unused and idle resources, right-sizing resources, automation, and cost analysis are effective for optimizing cloud resources and costs. Understanding the needs of organizations and businesses is crucial in designing and implementing cloud solutions that optimize their processes.
Automated Scaling automatically adopts all active instances according to real-time demand. Thus, auto-scaling ensures that businesses pay for what they use only while securing their services during peak times.
Load balancing distributes workloads throughout multiple resources, preventing bottlenecks because of overloads. This ensures application availability and responsiveness, offering users a high-quality service.
The DevOps advances collaboration between development and operations teams, contributing to faster and more reliable software delivery. DevOps teams improve cloud computing to automate testing, deployment, and monitoring to achieve efficiency and reduced time to market.
CI/CD pipelines offer automated application testing and deployment. This improves the development process and ensures code change integration, reducing the risk of errors and downtime.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization secures real-time control and constant improvement. They are essential for the efficient experience of cloud applications.
Data Lakes on AWS
Data lakes provide a flexible, scalable, and affordable way for organizations to store, process, analyze, and gain insights from data from diverse sources. Data lakes are popular for the advantages they offer organizations, from scalability to data security. The key features and benefits of data lakes on AWS include:
- Storage and Scalability: AWS-based data lakes store their data in Amazon S3, inheriting all its properties—durability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. They can store exabytes of data and support nearly unlimited storage.
- Flexible Data Ingestion: This is real-time data ingestion from databases, data warehouses, and streaming data. These systems support a wide array of data formats, such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Data Cataloging and Discovery: AWS Glue creates a data catalog to help users get access to relevant data. It provides a searchable, responsive interface to the data in the catalog.
- Security and Governance: Security and governance features such as access controls, encryption, and auditing. AWS Lake Formation facilitates setting up a secure data lake and managing it by automating those complicated manual tasks.
- Analytics and Machine Learning: Data lakes allow sophisticated analytics and machine learning on their data with the help of a variety of AWS services like Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, and Amazon SageMaker. They combine data from a number of sources, allowing users to train machine-learning models with better accuracy.
Emerging Trends and Future of Cloud Computing
- AI and Machine Learning Integration. Cloud services are increasingly deploying AI and ML to enhance data storage and optimization through process automation and AI-driven insights. With ML, cloud providers can offer clients predictive analysis, resource management, and enhanced security.
- Quantum Computing in the Cloud. Quantum processors offer computing beyond the capabilities of current computers. Access to lightning-fast processing power over the cloud will revolutionize many industries, helping organizations scale their products and services faster and more effectively.
- Sustainable and Green Cloud Computing. Renewable energy and sustainable practices are important in the cloud computing space as providers work towards sustainable goals. This is birthing carbon-neutral data centers and corporate social responsibility targeted at enhancing sustainability for cloud providers and clients.
- Edge-Cloud Convergence. Edge computing leverages a distributed computing framework for closer proximity of computing abilities, networks, and data to end users. Edge computing has become a driving force for IoT and is being adopted in cloud computing. Edge computing allows local data processing rather than transfers to centralized cloud servers. The edge-cloud convergence will enhance cloud computing services, reduce latency, enhance the speed of data-driven applications, and expand the capabilities of both technologies.
Conclusion
Cloud computing shapes current realities for businesses and organizations of all sizes and drives growth strategies. Through data lakes and edge computing, cloud users can enjoy fast and seamless access to secure data servers globally and optimize their processes for cost and efficiency.
References:
https://cybermagazine.com/cloud-security/history-cloud-computing
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/cloud-computing/deployment-models.html