Introduction
Hot tapping, also known as pressure tapping, is a sophisticated technique used in various industries, including oil and gas, water, and chemical processing. This process allows for the connection of new branches to existing pipelines or vessels without the need to shut down the system or interrupt the flow of the product. This capability is particularly valuable in industries where downtime can lead to significant financial losses or operational disruptions. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of industrial hot tapping, its applications, benefits, and the safety measures required to execute it effectively.
What is Hot Tapping?
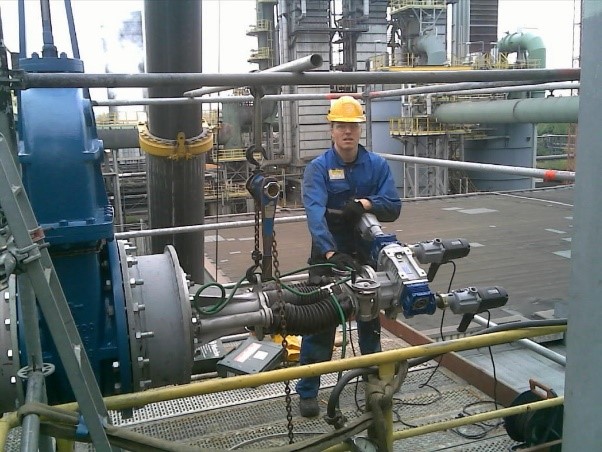
Hot tapping is a method that involves drilling or cutting into a live, pressurised pipeline or vessel to install a new branch connection. This procedure is performed using specialised equipment and techniques to ensure that the system remains operational and safe throughout the process. The primary components of a hot tapping operation include the hot tap machine, tapping fittings, valves, and a pilot drill.
Applications of Hot Tapping
Oil and Gas Industry: Hot tapping is widely used in the oil and gas sector to create new connections for pipelines transporting crude oil, natural gas, and other hydrocarbons. It enables operators to tie in new wells, perform repairs, or reroute flow without shutting down production.
Water Supply Systems: Municipal water supply networks often employ hot tapping to connect new service lines, perform maintenance, or expand the distribution network. This method ensures that water supply remains uninterrupted to consumers.
Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, hot tapping allows for the integration of additional processing units or the installation of new instrumentation without halting the chemical production process. This is crucial for maintaining continuous operation and meeting production targets.
Power Generation: Power plants, especially those utilising steam or other pressurised fluids, use hot tapping to make modifications or expansions to their piping systems. This helps in improving efficiency and adapting to changing operational requirements.
Benefits of Hot Tapping
Minimised Downtime: One of the most significant advantages of hot tapping is the ability to perform modifications without shutting down the system. This minimises downtime, which is particularly critical in industries where continuous operation is essential.
Cost Savings: By avoiding shutdowns, companies can save substantial amounts of money that would otherwise be lost due to halted production. Additionally, hot tapping reduces the need for extensive labour and materials associated with traditional shutdown and restart procedures.
Enhanced Safety: Hot tapping is designed to be a safe procedure when executed correctly. The use of specialised equipment and adherence to strict safety protocols ensures that the risk of accidents, such as leaks or explosions, is minimised.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Hot tapping provides the flexibility to make changes or expansions to existing systems without the need for extensive redesigns or reconstructions. This adaptability is crucial for industries that need to respond quickly to changing market demands or regulatory requirements.
The Hot Tapping Process
Planning and Preparation: The first step in hot tapping is thorough planning and preparation. This includes assessing the pipeline or vessel to determine the appropriate location for the tap, selecting the correct equipment, and ensuring all safety measures are in place. Engineers must also obtain necessary permits and conduct a risk assessment.
Installation of Tapping Fittings: Once the planning phase is complete, the next step is to install the tapping fittings. These fittings, often referred to as hot tap saddles or sleeves, are welded or clamped onto the pipeline at the designated location. They provide a secure attachment point for the hot tap machine.
Mounting the Hot Tap Machine: After the fittings are in place, the hot tap machine is mounted onto the fittings. This machine houses the cutting or drilling equipment needed to create the new connection. It is essential to ensure that the machine is correctly aligned and securely attached.
Performing the Tap: With the hot tap machine in place, the actual tapping process begins. A pilot drill is used to make an initial hole in the pipeline or vessel. Once the pilot hole is complete, a larger cutter is used to create the full-size opening. During this process, the system remains pressurised, and the product continues to flow through the pipeline.
Installing the Valve and Branch Connection: After the tap is complete, a valve is installed to control the flow through the new connection. The new branch line is then attached to the valve, completing the hot tapping operation. The valve allows for the branch line to be isolated or integrated into the system as needed.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in hot tapping operations due to the inherent risks of working with pressurised systems. Several key safety considerations must be addressed:
Personnel Training: All personnel involved in hot tapping operations must be adequately trained and knowledgeable about the equipment, procedures, and potential hazards. This includes understanding the specific requirements of the system being tapped.
Equipment Inspection: Regular inspection and maintenance of hot tapping equipment are crucial to ensure that it is in good working condition. Any defects or malfunctions can lead to dangerous situations during the tapping process.
Pressure Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of system pressure is essential during hot tapping. Any significant pressure fluctuations or abnormalities must be addressed immediately to prevent accidents.
Emergency Preparedness: A comprehensive emergency response plan must be in place in case of unexpected incidents. This includes having firefighting equipment, spill containment measures, and evacuation procedures readily available.
Conclusion
Hot tapping is a vital technique that allows industries to modify and expand their operations without interrupting the flow of product or incurring significant downtime. Its applications are diverse, spanning the oil and gas, water supply, chemical processing, and power generation sectors. By following stringent safety protocols and utilising specialised equipment, hot tapping can be performed safely and efficiently. As industries continue to evolve and demand greater flexibility, hot tapping will remain an essential tool in the maintenance and expansion of critical infrastructure.