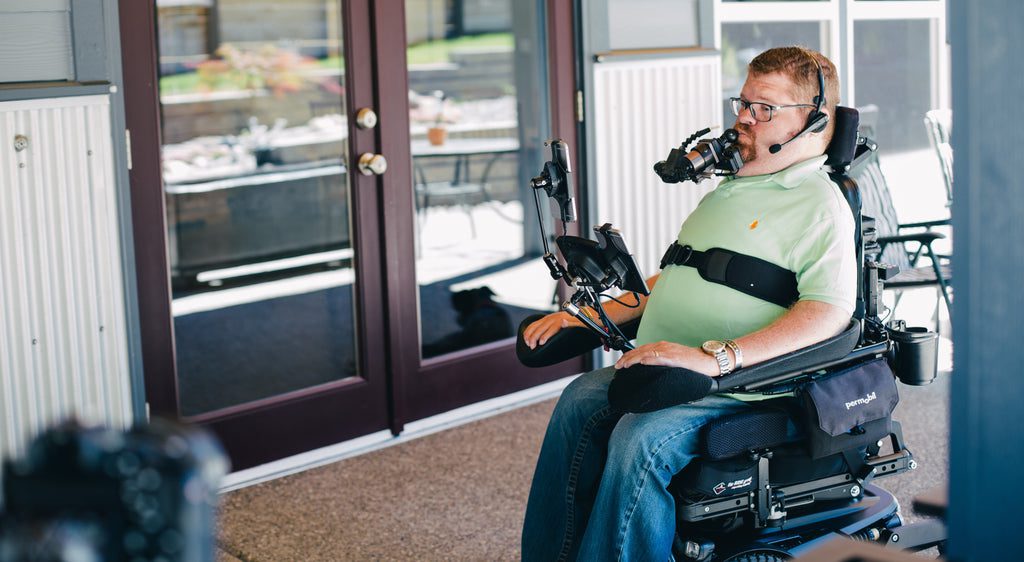
As the population continues to age and technological advancements in mobility devices increase, the need for accessible housing has become more critical than ever. For individuals who rely on mobility devices such as wheelchairs and electric power chairs, accessibility features are not just a matter of convenience but a necessity for independent living. In many jurisdictions, laws and regulations mandate specific accessibility requirements to ensure that homes are designed to accommodate these needs. In this article, we will explore the essential accessibility requirements mandated by law for housing construction, specifically focusing on accommodating mobility devices and electric wheelchairs.
Understanding Accessibility Requirements:
Accessibility requirements for housing construction are primarily governed by building codes and standards established at the local, state, and federal levels. These regulations aim to ensure that homes are designed and built in a manner that allows people with disabilities to live comfortably and safely. While specific requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction, there are several common accessibility features that are universally mandated. These include:
- Entrances and Exits: All entrances to the home, including front doors, back doors, and garage entrances, must be designed to accommodate wheelchairs and other mobility devices. This typically involves the installation of ramps with specific slope requirements and wide enough doorways to allow for easy passage.
- Interior Doorways and Hallways: Inside the home, doorways and hallways should be wide enough to accommodate the turning radius of a wheelchair or power chair. The minimum width requirement often ranges from 32 to 36 inches to ensure smooth navigation throughout the house.
- Accessible Bathrooms: Bathrooms are one of the most critical areas of the home to consider for accessibility. Requirements may include installing grab bars near the toilet and shower, ensuring roll-in showers or transfer showers are available, and providing sufficient space for maneuvering within the bathroom.
- Kitchen Accessibility: In the kitchen, countertops should be at a height that allows individuals in wheelchairs to comfortably prepare meals. Additionally, there should be clear floor space to allow for easy maneuverability, and appliances should be easily reachable from a seated position.
- Flooring and Surfaces: Flooring surfaces should be slip-resistant and smooth to allow for easy movement of wheelchairs and power chairs. Carpeting should be low-pile to minimize resistance, and thresholds between rooms should be flush to prevent tripping hazards.
- Accessible Controls and Fixtures: Light switches, electrical outlets, thermostats, and other controls should be placed at a height that is easily reachable from a seated position. Additionally, lever-style door handles are often preferred over traditional knobs for ease of use.
Integrating Accessibility Requirements into Home Construction:
Incorporating accessibility requirements into the design and construction process of a home requires careful planning and coordination among architects, builders, and contractors. Here are some key steps to ensure compliance with accessibility standards:
- Early Planning and Design: Accessibility should be considered from the initial stages of the design process. Architects and designers should work closely with accessibility experts to create floor plans that prioritize functionality and ease of use for individuals with disabilities.
- Collaboration with Contractors: Builders and contractors play a crucial role in implementing accessibility features during the construction phase. Clear communication and collaboration between all parties involved are essential to ensure that design specifications are accurately translated into built form.
- Quality Materials and Construction: Using high-quality materials and construction techniques is essential to ensure that accessibility features are durable and long-lasting. This includes properly installing ramps, grab bars, and other fixtures according to manufacturer guidelines and building codes.
- Regular Inspections and Compliance Checks: Throughout the construction process, regular inspections should be conducted to verify compliance with accessibility requirements. This may involve working closely with building inspectors and accessibility consultants to address any issues or discrepancies that arise.
Benefits of Accessibility in Home Construction:
While integrating accessibility requirements into home construction may require additional time and resources, the benefits far outweigh the costs. By creating homes that are accessible to individuals with disabilities, builders can:
Expand the market for their properties by appealing to a broader range of potential buyers. Enhance the overall livability and comfort of the home for all occupants, regardless of age or ability. Promote inclusivity and diversity within communities by fostering environments that are welcoming to people of all backgrounds and abilities.
In conclusion, incorporating accessibility requirements for mobility devices and electric power wheelchairs into home construction is not only a legal obligation but also a moral imperative. By ensuring that homes are designed and built with the needs of individuals with disabilities in mind, builders can create environments that promote independence, dignity, and inclusivity for all. Through careful planning, collaboration, and adherence to building codes and standards, we can create a future where accessible housing is the norm rather than the exception.