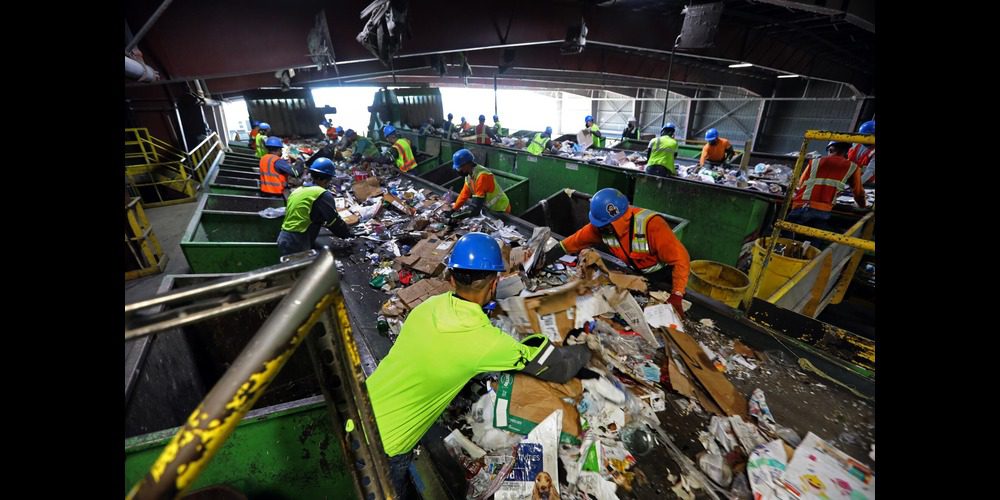
People go berserk every time a big brand launches a new smartphone and other devices with the promise of some crazy upgrades. They make it a goal to gift themselves one before the holiday season. But do you realize it adds up to the growing electronic waste problem? Most of the latest tech gadgets come with a short lifespan, and the option to repair old systems is also rapidly declining. All these together contribute to the massive piling of e-waste. In 2019, about 53.6 million metric tons of electronic waste was dumped, of which 17.4% went for recycling. Can you imagine its impact? The concern around e-waste transcends the habit of hoarding and crowding space in the junk drawers.
The American Environmental Protection Agency informs that giant e-waste burdens landfills in developing countries lacking facilities to handle or recycle them. WHO added that young children deal with these e-waste matters in those countries to recover copper, palladium, silver, and other valuable metals. Due to this, over 18 million kids face adverse health effects. If you want to do something in this area, increase your awareness about the best practices to manage household waste, specifically e-waste, which tends to be hazardous. Do you live in Oahu? You can contact Oahu’s best junk removal company for assistance. Before this, let’s understand e-waste more.
- E-waste Overview
E-waste includes old, malfunctioning, and expiring or dying electronic devices. Fax machines, copiers, computers, stereos, speakers, and televisions are those commonly used items. The concerns around e-waste management have been there even in the 1970s. However, the scene has dynamically changed today with the number of these items discarded daily. So, e-waste stands for any discarded electronic or electrical equipment that is broken or working. You donate them to a charity or add them to your garbage. Many people may need to learn that even unsold devices in retail stores are dumped in landfills. E-waste requires a proper disposal approach because of the toxic chemicals it leaches when buried. They contain zinc, lead, cadmium, nickel, mercury, beryllium, etc. Some sources indicate that old televisions and CRT monitors comprises around 4 pounds of lead.
- Types of e-waste
Most homes use entertainment devices, communication & IT equipment, and electronic utilities. Hence, it’s common to find heaters, electric cookers, fans, smartphones, computers, laptops, circuit boards, hard drives, stereos, televisions, DVDs, video game systems, heating pads, massage chairs, remote controls, lamps, treadmills, smartwatches, printers, Wi-Fi dongles, and many more. You can group these into different categories to ensure proper disposal. For instance, large appliances like stoves, air conditioners, washing machines, refrigerators, and others are classified as Category 1 e-waste. Under Category 2, the list includes toasters, microwaves, and vacuum cleaners. Mainly, smaller appliances belong here. Category 3 of e-waste comprises laptops, phones, tablets, and computers. In Category 4, video cameras, audio devices, monitors, and televisions come.
- E-waste disposal
Consumers’ fascination with new devices will make them buy more such products. While it is challenging to control this urge, some thoughtful disposal efforts can be appreciated. One can give their devices for recycling instead of junking them. If you know any local firms specializing in this, you can contact them. Or, the most convenient way is to rope in a local junk remover, who can send equipment to a recycling facility. In this case, you only need to collect your unused electronic devices in one place. Store them in a trash bin or can. Bulky items would demand more space. You can put them in a garage in one corner. After you accumulate everything, you can talk to your junk removal company for pickup.
When you call them, you can enquire about the types of discarded e-waste items they usually accept. A reputable organization deals in most products, such as laptops, headphones, television sets, cell phones, speakers, extension cords, ACs, lamps, and printers. Since you already know the devices you desire to eliminate after that cleanup, you can specify those for clarity. Get their quotes and ensure you ask them about the recycling process. After all, that’s the main thing. A responsible junk removal service provider will always try its best to send most digital rubbish to recycling. Why should there be an emphasis on recycling?
As hinted earlier, electronics contain chemicals. At the same time, these items are produced from glass, plastics, metals, and other resources obtained from mining. When everyone chooses recycling as an option, it helps in conserving resources. Water and air pollution risks are also reduced significantly. According to a geological survey, upcycling or renewing 1 million laptops can help save an adequate amount of energy used by over 3,500 homes annually. If you recycle 1 million cell phones, you save palladium (33 pounds), silver (772 pounds), copper (35k pounds), and gold (75 pounds).
- Safe e-waste handling practices
Before putting them into a bin, you must take out all lithium-ion-based batteries. Lithium-ion can cause a fire hazard in a garbage truck due to compression. Hence, you should remove them before putting the devices in the house waste or recycling bin. At the same time, remember to erase all personal details from the devices, such as bank accounts, social media account passwords, e-shops, etc. Everyone must take this precaution to prevent data theft, which is familiar with e-waste disposal. Deleting all the details from these devices is like shredding critical documents that contain your address, contact, bank information, security number, etc. Nobody can impost your identity or use your credit card. So, be careful whether you donate, recycle, or discard your laptop or phone.
Someone can leverage the smartphone’s memory stick or your laptop’s hard drive if you miss this. All these impostors need to do is plug them into another compatible device. Hence, dismantle the electronic items properly. A casual approach can prove risky because you deal with highly explosive batteries.
- E-waste recycling process
It is a complex method compared to traditional waste restoration. It starts with sorting all the items manually. When they reach a facility, workers divide the discards into different categories based on models and types. Each product is inspected to identify the functional parts and extract them safely for reuse. These parts are then sold individually or as a component of a new computer or phone in the market. The leftover items go to the recycling process. These are fed into a gigantic machine to be reduced to tiny pieces. Remember, only disassembled parts go into the machine, not an entire product, such as a fridge, television, etc. This step is called de-manufacturing. At this stage, technicians eliminate any hazardous material in the devices to protect the machine and the environment from contamination risks.
If you use a photocopier, it’s helpful to know that this equipment contains extremely inflammable and fiery material called toner. If the copier is put into the recycling processing machine without removing this part, it will most likely explode during shredding. The probability of such an incident is high because of the availability of plastic and other fuel sources. Only experts can handle this aspect well. After shredding, the precious metal parts are separated. Recycling companies rely on them for their profitability. This process uses an enormous magnet to attract steel, iron, and other magnetic materials. In another automatic process, alloys and metals are sorted out.
The extensive procedure also consists of using water to separate the waste. After all the efforts, only non-magnetic materials will be there. These will go for water treatment, enabling glass to sink and low-density products like plastic to flow. Before selling the recycled products, professionals will ensure all the valuable parts have been removed from the plastic.
- The benefit of recycling e-waste
E-waste restoration is environmentally friendly. It protects human bodies from toxic materials and natural resources from depleting due to intensive mining activities. The recycling industry also adds to the economic growth of the countries. In 2019, the value of the unused e-waste soared to over US $57 billion.
- The need to be self-conscious about e-waste
If you look into most e-waste items today, they are more than merely malfunctioning or obsolete devices. The technologically advanced equipment is replacing its predecessors at a dizzying speed. Hence, what you stop using is not necessarily a damaged or non-working device. Think of VCR, DVD, and Blu-ray players and how one made the other redundant. And this e-waste is created every time someone tries to build an upgraded version of an existing item. As a wise citizen and inhabitant of Earth, everyone should care about this because unwanted electronics quickly fill landfills worldwide. America’s Environmental Protection Agency data show that around 60 million metric tons of such waste is dumped annually in US landfills.
Buying or investing in new products is a good habit as long as it is done with mindfulness. The urge should be driven more by necessity than stature or fashion goals. If you wait for the items to become obsolete naturally through regular use, it can significantly help. Of course, irreparable or low-performing systems will have to be shunned. So, there is no need to feel guilty about that.
Read More From Techbullion